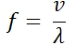
The equation for frequency is:
Where:
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
λ = wavelength (m)

Speed, frequency and wavelength calculators


Advertisement





Calculator


Speed, Frequency and Wavelength
This page contains a frequency calculator, as well as calculators with the equation rearranged to make speed and
wavelength the subject. The formulas are shown together with other useful information and examples to try. Unit
converters (feet to metres and so on) can be found here (opens in a new tab).
Note that when considering electromagnetic radiation, such as light, the quantity speed is usually denoted by the letter
c, but otherwise the letter v (standing for velocity) is usually used. We will use v on this page in all cases, which is
measured in metres per second (m/s).
Frequency (f)
The equation for frequency is given on the upper right.
Example: A particular AM radio station uses a wavelength of 250
metres. What frequency do we need to tune our receiver to in order to
hear the broadcast?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, so in this case v is equal to
299,792,458 metres per second (m/s). Putting these figures (without
commas) into the calculator above shows that we need to tune the
radio receiver to 1199.2 kHz (or 1.1992 MHz), which is around the
middle of the medium wave (MW) band.
Wavelength (λ)
The equation for wavelength is given above right.
Example: Microwave ovens use electromagnetic radiation with a
frequency close to 2.45 GHz to heat up food. What is the wavelength
of the radiation?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, so in this case v is equal to
299,792,458 metres per second (m/s), and 2.45 GHz is 2,450,000,000
Hz, so that’s the frequency. Putting these figures (without commas)
into the calculator above shows that the wavelength is 0.122 metres,
or 12.2 centimetres.
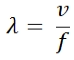
The equation for wavelength is:
Where:
λ = wavelength (m)
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)

Velocity (v)
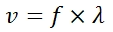
The equation for velocity is:
Where:
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)
λ = wavelength (m)
The equation for velocity is given above right.
Example: Sound travels in waves and does so at a particular speed
depending on what it is travelling through, such as air, brick or water.
To find the speed of sound in air we can note that the musical note A
above middle C has a frequency of 440 Hz and a wavelength of 0.773
metres. Putting these figures into the calculator above shows that the
speed of sound in air is close to 340.1 meters per second.

Common metric prefixes
kilo (k): 1,000 (thousand)
mega (M): 1,000,000 (million)
giga (G): 1,000,000,000 (billion)
Other metric prefixes are listed here.
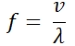



Calculator
Advertisement



Speed, Frequency and Wavelength
Speed, frequency and wavelength calculators
This page contains a frequency calculator, as well as calculators
with the equation rearranged to make speed and wavelength the
subject. The formulas are shown together with other useful
information and examples to try. Unit converters (feet to metres
and so on) can be found here (opens in a new tab).
Note that when considering electromagnetic radiation, such as
light, the quantity speed is usually denoted by the letter c, but
otherwise the letter v (standing for velocity) is usually used. We
will use v on this page in all cases, which is measured in metres
per second (m/s).

Frequency (f)
The equation for frequency is given below.
Example: A particular AM radio station uses a wavelength of
250 metres. What frequency do we need to tune our receiver to
in order to hear the broadcast?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, so in this case v is
equal to 299,792,458 metres per second (m/s). Putting these
figures (without commas) into the calculator above shows that
we need to tune the radio receiver to 1199.2 kHz (or 1.1992
MHz), which is around the middle of the medium wave (MW)
band.
The equation for frequency is:
Where:
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
λ = wavelength (m)
Wavelength (λ)
The equation for wavelength is given above right.
Example: Microwave ovens use electromagnetic radiation with a
frequency close to 2.45 GHz to heat up food. What is the
wavelength of the radiation?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, so in this case v is equal
to 299,792,458 metres per second (m/s), and 2.45 GHz is
2,450,000,000 Hz, so that’s the frequency. Putting these figures
(without commas) into the calculator above shows that the
wavelength is 0.122 metres, or 12.2 centimetres.
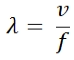
The equation for wavelength is:
Where:
λ = wavelength (m)
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)
Velocity (v)
The equation for velocity is given above right.
Example: Sound travels in waves and does so at a particular
speed depending on what it is travelling through, such as air, brick
or water.
To find the speed of sound in air we can note that the musical
note A above middle C has a frequency of 440 Hz and a
wavelength of 0.773 metres. Putting these figures into the
calculator above shows that the speed of sound in air is close to
340.1 meters per second.
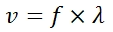
The equation for velocity is:
Where:
v = velocity (m/s, ms
-1
)
f = frequency (s
-1
, or Hz)
λ = wavelength (m)
